Table of Contents
ToggleWhen we think of electric vehicles (EVs), what comes to mind is their seamless operation, impressive efficiency, and contribution to a cleaner, greener planet.
But have you ever wondered what powers these vehicles and how they convert electrical energy into the mechanical energy needed to drive them? The answer lies in a crucial component: the electric motor.
Understanding the Role of Electric Motors
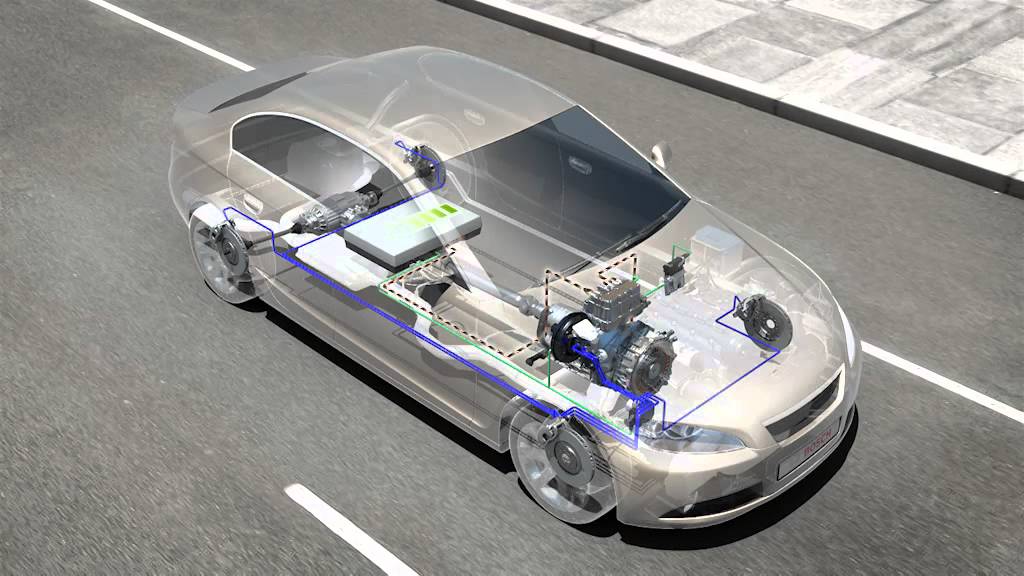
At the heart of every EV is an electric motor, a device designed to convert electrical energy—stored in the vehicle’s battery—into mechanical energy that drives the wheels. This process is not only efficient but also remarkably silent compared to traditional internal combustion engines (ICEs).
Electric motors work based on electromagnetic principles, where electric current flowing through coils of wire generates a magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with another magnet (permanent or electromagnet) in the motor to create motion. This motion is harnessed to spin the EV’s wheels, propelling the vehicle forward.
Types of Electric Motors Used in EVs
Electric vehicles typically use one of three main types of motors:
- DC Motors: These were among the first motors used in early EVs. While simple and reliable, they are less common today due to the availability of more efficient alternatives.
- Induction Motors (AC Motors): Pioneered by Tesla, induction motors are robust and efficient. They work without the need for permanent magnets, relying on electromagnetic induction to generate motion.
- Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSMs): These are widely used in modern EVs for their compact size, high efficiency, and excellent torque delivery. They rely on strong permanent magnets to create the magnetic field needed for rotation.
How the Conversion Happens
The process of converting electrical energy into mechanical energy begins with the EV’s battery, which supplies electricity to the motor. A power electronics unit, called an inverter, converts the direct current (DC) from the battery into alternating current (AC) if the motor requires it. The motor then generates rotational force (torque) to turn the wheels, translating electrical energy into motion.
Why Electric Motors Are Revolutionary
Electric motors are incredibly efficient compared to ICEs. While traditional engines lose a significant portion of energy to heat and friction, electric motors can achieve efficiencies of up to 90%. This efficiency not only reduces energy waste but also lowers the cost of operation and the environmental impact of driving.
Final Thoughts
The electric motor is the unsung hero of the electric vehicle revolution. By converting electrical energy into mechanical energy with remarkable efficiency, it enables a cleaner and more sustainable mode of transportation. As technology advances, we can expect even more sophisticated and efficient motors, further pushing the boundaries of what EVs can achieve.
So, the next time you see an electric vehicle gliding down the road, remember the marvel of engineering that makes it all possible—the electric motor.